Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) Occurs When Bacteria No Longer Responds To Antimicrobial Medicines
As a result of antimicrobial resistance, antibiotics become ineffective and infections become difficult or impossible to treat, increasing the risk of disease spread, severe illness, disability and death1

AMR is one of the top global public health threats
Global Deaths
Contributing Factor
associated deaths with antimicrobial resistance1
Economic Impact
US Infections
Antibiotic misuse is the main driver in the development of drug-resistance pathogens. Approximately 30%-50% of antibiotics prescriptions are unnecessary in U.S. doctor’s offices and ED.4
We can save 92 million lives between now and 2050 if we make a change now!9

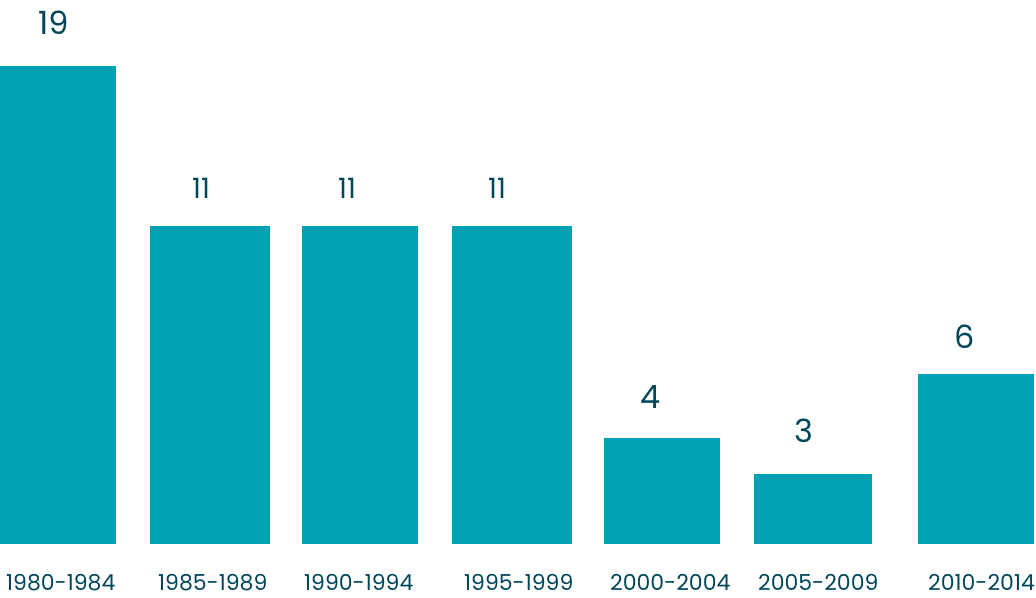
A Three Decade Decline In New Antibiotic Development
The number of new antibiotics developed and approved has decreased steadily over the past three decades, leaving fewer options to treat resistant bacteria.5
MeMed BV Can Help Fight AMR!
Accurately distinguishing between bacterial and viral infections, aiding physicians in making informed treatment decisions, including appropriate antibiotic use and the reduction of unnecessary prescriptions6,7,8

References
1. World Health Organization(WHO)/Antimicrobial resistance. Updated 21 November 2023. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antimicrobial-resistance
2. Thiruchelvi Pulingam et al, Antimicrobial resistance: Prevalence, economic burden, mechanisms of resistance and strategies to overcome,European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2021.106103.
- 3. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 2019 Antibiotic Resistance Threats Report. Updated March 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/antimicrobial-resistance/data-research/threats/index.html
4. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Outpatient Antibiotic Prescribing In the United States. Updated April 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/antibiotic-use/hcp/data-research/antibiotic-prescribing.html
5. Ventola CL. The antibiotic resistance crisis: part 1: causes and threats. P T. 2015 Apr;40(4):277-83. PMID: 25859123; PMCID: PMC4378521. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4378521/
6. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Transatlantic Taskforce on Antimicrobial Resistance (TATFAR). Updated April 2024 https://www.cdc.gov/tatfar/php/about/index.html
7. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Antimicrobial Resistance Investment Map and Funding. Updated May 2024 https://www.cdc.gov/antimicrobial-resistance/programs/AR-investment-map.html
8. World Health Organization(WHO). Global action plan on antimicrobial resistance https://apps.who.int/gb/ebwha/pdf_files/WHA68/A68_R7-en.pdf
9. GBD 2021 Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance 1990-2021: a systematic analysis with forecasts to 2050. The Lancet, Volume 404, Issue 10459, 1199 – 1226
